Introduction to 3D Printing
3D printing is an innovative technology whereby three-dimensional items are printed from digital designs. Unlike the traditional manufacturing method that typically consists of a process of cutting or molding materials, it builds objects in layers with different kinds of materials, such as plastic, metal, or resin. It is a ground-breaking process that has transformed industries with its unparalleled design flexibility, rapid prototyping, and cost-effective production. First conceptualized in the 1980s, this technology has evolved from a niche technology to a mainstream manufacturing tool used across multiple industries.
How it Works
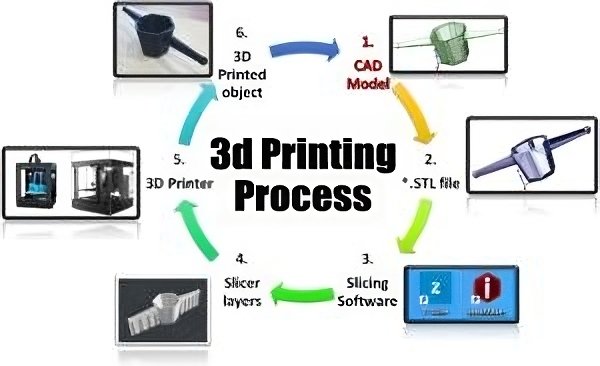
A digital 3D model is initially created using computer-aided design software, followed by the slicing of the model into very thin layers that the 3D printer can read as instructions for building the object from its very bottom. From entry-level machines with plastics, highly advanced systems printing with metals, ceramics, and even biological materials, 3D printers of many types are being put on the market. Commonly used printing materials include PLA-a biodegradable plastic, ABS-a tougher plastic, resin, and other specialized composites depending on printer and application.


Applications of 3D Printing
The versatility of 3D printing has found its application in many industries. It enables the manufacture of personalized prosthetics, implants, and even bioprinted tissues in medical care. In the automotive industry, 3D Printing is used for rapid prototyping, reducing development time for new parts. The technology also sipped into the fashion world, creating intricate designs and accessories impossible to achieve with traditional manufacturing. Indeed, from aerospace to education, innovative projects keep on demonstrating the transformative potential of 3D printing.

Step-by-Step Guide to 3D Printing
If you’re new to 3D printing, the process can seem daunting, but it’s relatively straightforward once you break it down:
- To anyone who has never used 3D printing, it seems to be such a daunting process, but really, it’s quite simple once it’s broken down:
- Design Your Object: More simply put, just make a design of an object you want using 3D modeling software, such as Tinkercad, great for beginners, and Blender, great for pros.
- Slice Your Design: This is the step in which the slicing software will take your 3D model and process it into layers that the printer will read. Common options include Cura and PrusaSlicer.
- Choose the Printer Setting: Based on the complexity of your design, choose material, layer height, infill percentage among other settings.
- Begin Printing: Feed the filament or the material in your printer, upload the file, and let the magic begin – watching an object grow layer by layer.
- Post-processing: After printing, one may need to remove the support structure or do some polishing in order to get a smooth finish.
Comparison of 3D Printers
Now, with the increased popularity of 3D printing technology, there are a number of printers available for both beginners and pros. For example, models like the Creality Ender 3 and Prusa i3 MK3S+ are popular entry-level printers that are quite budget-friendly and easy to work with while giving very good print quality. More professional printers, such as the higher scaled-up versions like the Ultimaker S3 and Formlabs Form 3, even boast better advanced features like dual extrusion, greater material compatibility, and great detail accuracy. Selection criteria of a printer have to be considered in view of the volume of build, material compatibility, ease of use, and budget.


Future of 3D Printing
The future of 3D printing is bright, with new developments yet to come. The latest trends include multi-material printing, which enables one to make objects with complex properties, and bioprinting, which can enable the printing of functional organs for medical use. Besides that, the constant development of faster and more accurate printers contributes much to reducing production times and costs, hence turning it into an even more feasible alternative for mass production.
Challenges and Solutions
With all the pros that come with 3D printing, there are, of course, cons to consider. These include warping, that is, your print does not lie flat; issues with proper adhesion of the layers; and prints that simply do not turn out right because of incorrect settings. Many of these problems can be conquered with correct calibration of your printer, high-quality materials, and basic troubleshooting.

